Describe the Organization of the Eukaryotic Chromosome.
Centromeric DNA and artificial chromosomes. Describe the organization of the eukaryotic chromosome.
9 - Describe the structure and complementary base.
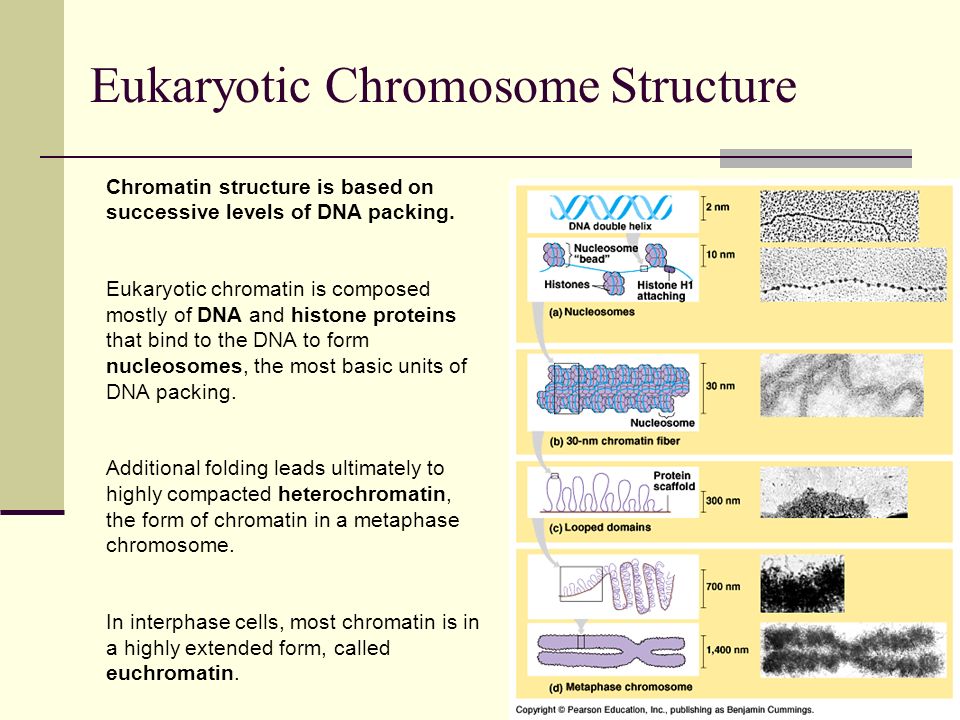
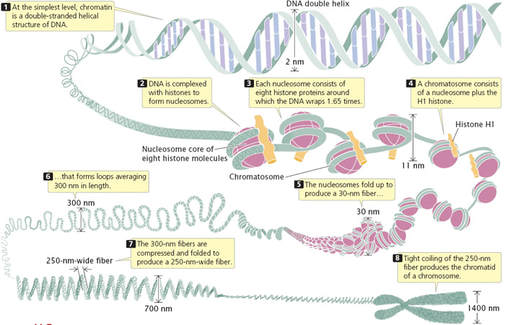
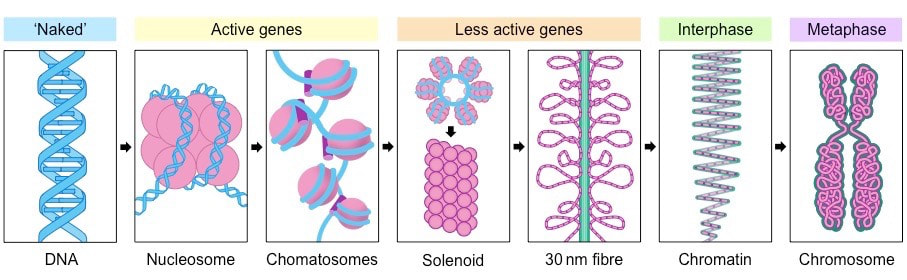
. Eukaryotic chromosomes are much larger in size and requires special proteins called histone proteins which forms a special structure called nucleosomes when DNA is wrapped. Compared to prokaryotic chromosomes eukaryotic chromosomes are much larger in size and are linear chromosomes. Ii the solenoidal or superbead nucleomere model of compactization of the nucleosomal fiber.
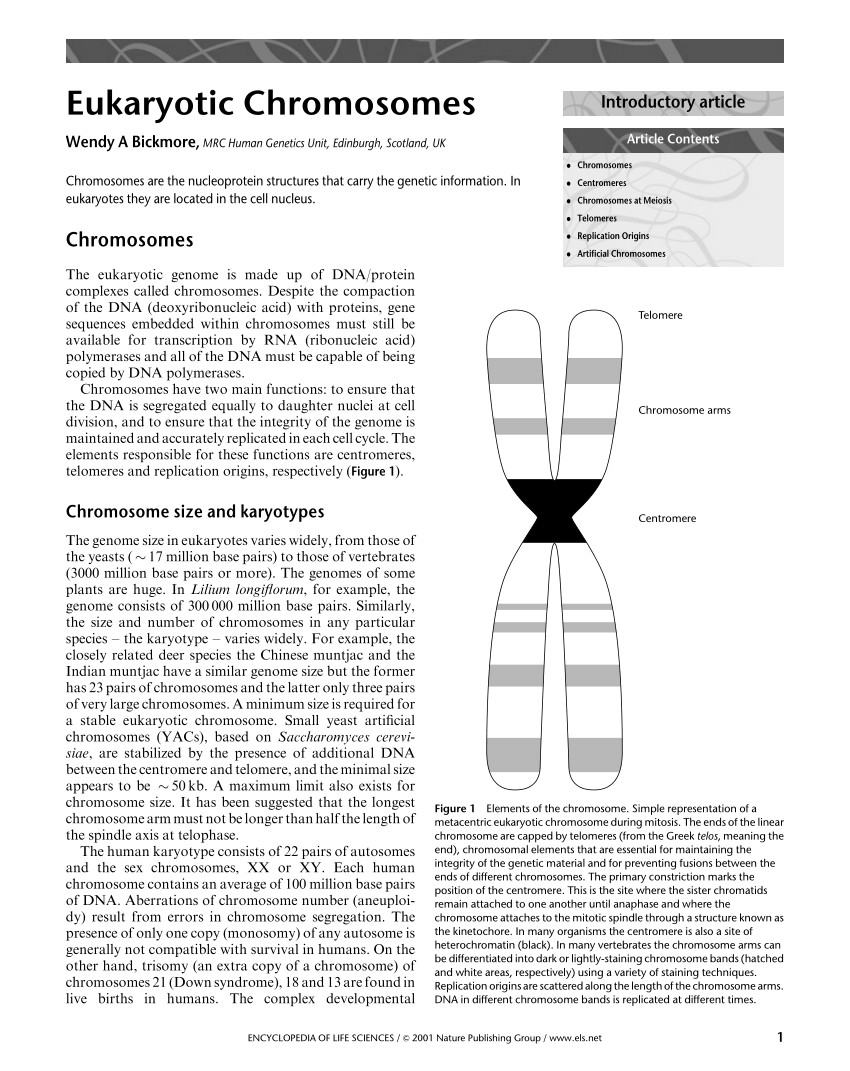
Three levels of structural organization of eukaryotic DNA in the cell nucleus are considered in this paper. Eukaryotic chromosomes consist of a DNA-protein complex that is organized in a compact manner which permits the large amount of DNA to be stored in the nucleus of the cell. 1Describe one structural feature of the telomeres located at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes.
- there is a stretch of unwound DNA between each nucleosome. The DNA is wound around proteins called histones. - octamer eight protein complex.
9 - Transcribe and translate the following DNA. I the chain of nucleosomes. Where are genes primarily located relative to chromosome structure.
Eukaryotic chromosomes consist of a DNA-protein complex that is organized in a compact manner which permits the large amount of DNA to be stored in the nucleus of the cell. DNA is wound around histone proteins to produce nucleosomes. The packaging of the chromosome in prokaryotic cell is rather simpler then the eukaryotic cell.
The whole DNA in our nucleus is assembled into number of chromosomes. Describe the general organization of a bartleby. At the most basic level a chromosome is a molecule of DNA that is tightly coiled around proteins called histones.
- has 2 copies of H2A H2B H3 H4. Chromosomes are condensed chains of DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid. In order for the chromosome to fit into the microscopic nucleus eukaryotic chromosomes have developed a mechanism to condense and organize the DNA into structures called chromosomes.
9 - How do the linear chromosomes in eukaryotes ensure. Describe the general organization of a eukaryotic chromosome. Double layered membrane covering nucleus is known as nuclear membrane which is structurally different to that of plasma membrane.
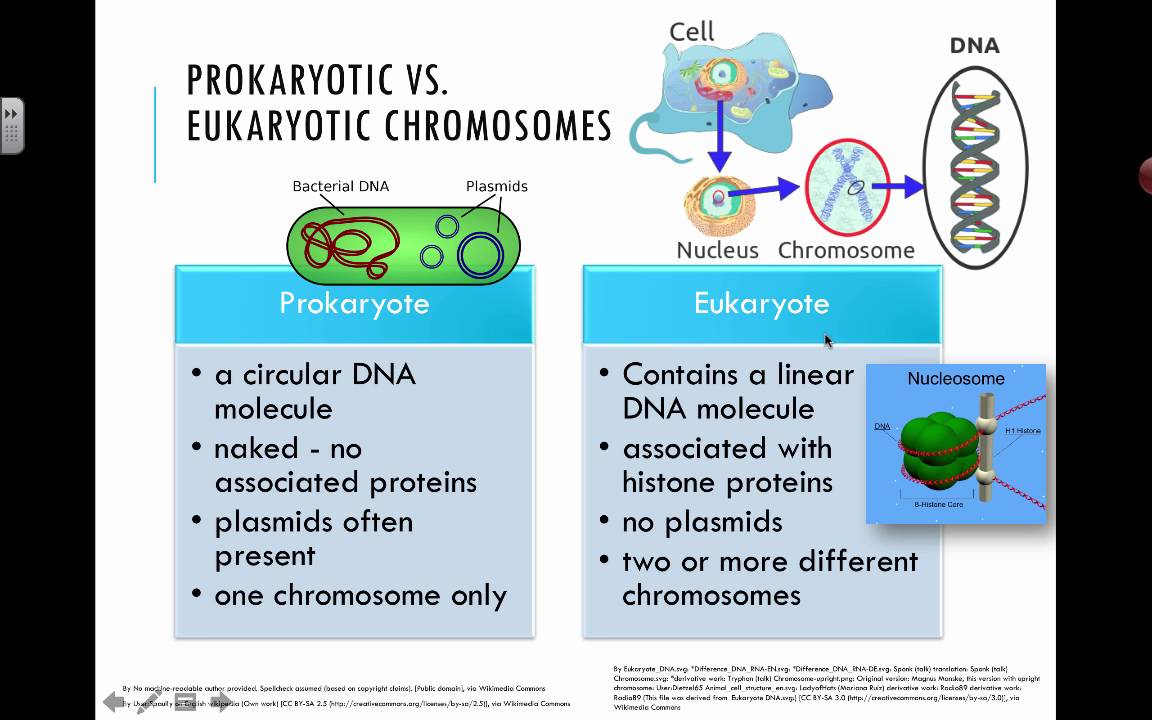
Eukaryotic chromosome structure refers to the levels of packaging from raw DNA molecules to the chromosomal structures seen during metaphase in mitosis or meiosis. Unlike prokaryotic chromosomes eukaryotic chromosomes are made up of a single linear DNA molecule. School Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University.
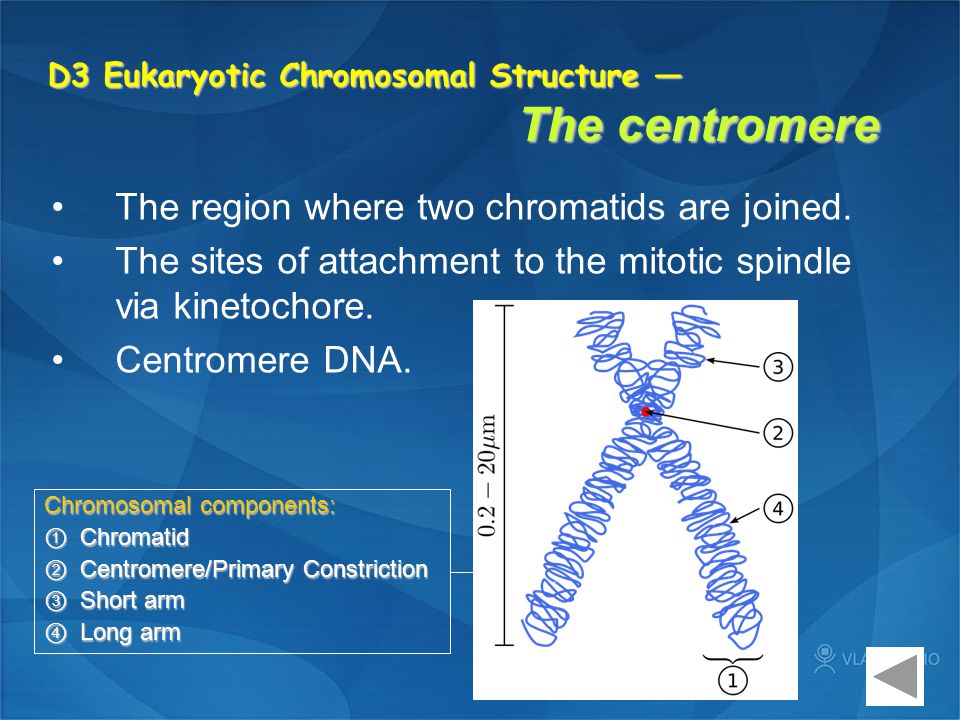
The histones play an important role in determining of eukaryotic chromosomes by determining the conformation known as chromatin. Describe one of the practical applications of the Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR. The centromere is an essential structural component of the eukaryotic chromosome and is required for faithful segregation in mitosis and meiosis.
Organization of Eukaryotic Chromosomes Each eukaryotic chromosome consists of a single extremely long molecule of DNA. Describe the function of the telomerase enzyme. Eukaryotic cells have multiple chromosomes that are linear in shape.
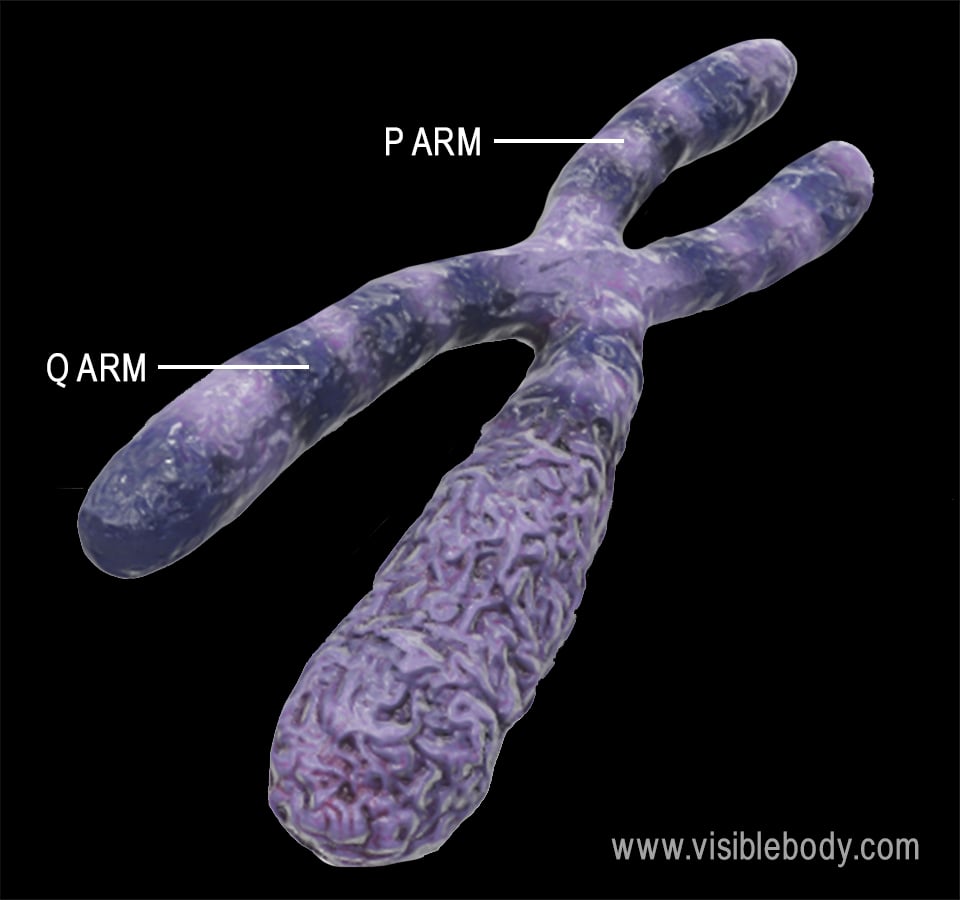
Chromosomes are essentially located in the nucleus which is double layered cell organelle. The following illustration explores the shape classification and features of a eukaryotic chromosome. For all of this DNA to fit into the nucleus tremendous packing and folding are required The chromosomes are in an elongated relatively The chromosomes are in an elongated relatively.
- 146 BP of supercoiled DNA. The fiber is further coiled for greater compactness. The whole DNA in our nucleus is assembled into number of chromosomes.
9 - Describe how. Course Title BIO MISC. The histones then stack together in a compact form that creates a fiber that is 30-nm thick.
Ratings 100 1 1 out of 1 people found this document helpful. 12 describe the organization of the eukaryotic. Biology questions and answers.
The subunit designation of the chromosome is chromatin. The tight coiling and high degree of organization in this supercoiled DNA facilitate proper segregation during mitosis and cell division. The term centromere refers to the.
The nucleosomes are the repeating units of DNA organization which are often termed as beads. - wrapped around a core of 8 histone molecules. 9 - Describe the organization of the eukaryotic.
What structural role do scaffold associated regions SARs or matrix attachment regions MARs play. This preview shows page 3 out of 3 pages. Prokaryotic chromosome is packed with the help of nucleoid associated proteins which helps in packaging.
Describe what happens during each of the three steps of a PCR reaction cycle. Each chromosome contains a molecule of DNA that is wound tightly around clusters of histone proteins. During cell division eukaryotic chromosomes condense into highly coiled structures.
Iii the mode of suprasolenoidal DNP-packing--loops or domains. Chromosomes contain long strands of DNA containing genetic information. The DNA inside the nucleus is organized into chromosomes.
Topic 3 2 Chromosomes Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green

Chromosome Structure Biology For Majors I
Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Chromosomes 2016 Ib Biology Youtube

Lesson Explainer Dna In Eukaryotes Nagwa
Section D Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure Ppt Video Online Download
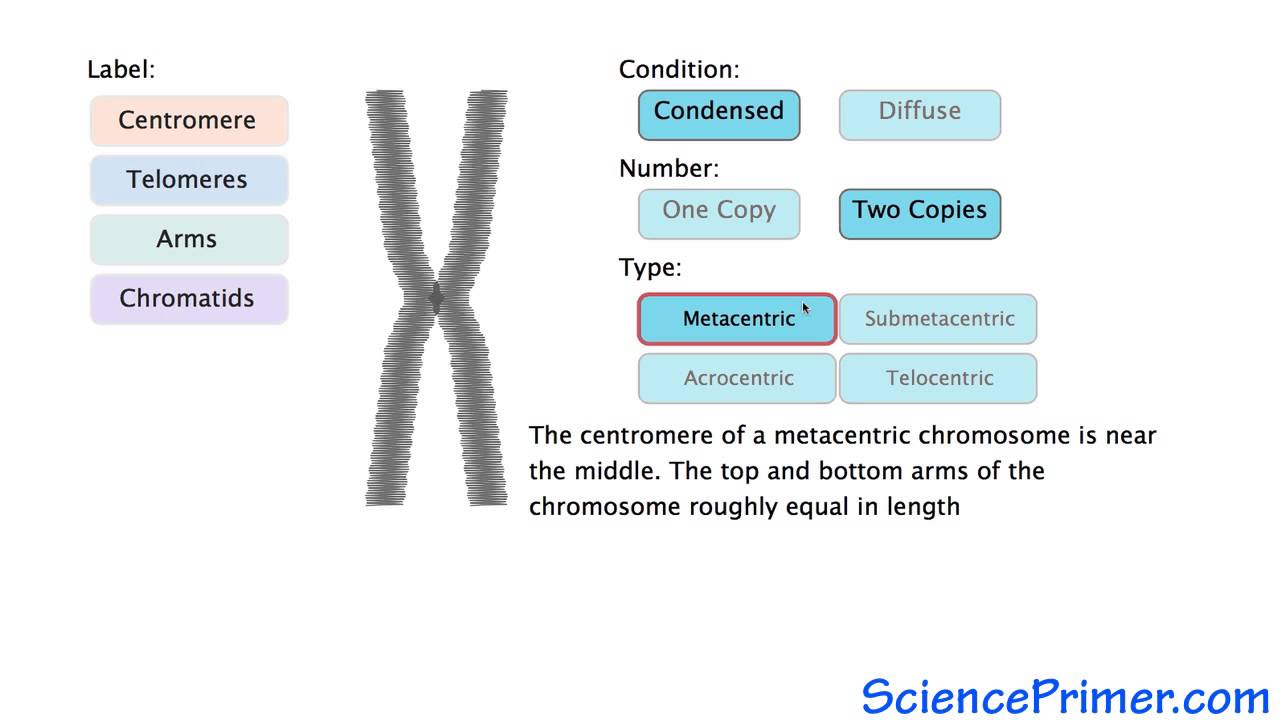
Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure Overview Youtube
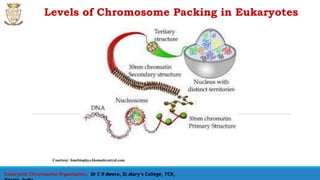
Eukaryotic Chromosome Organisation
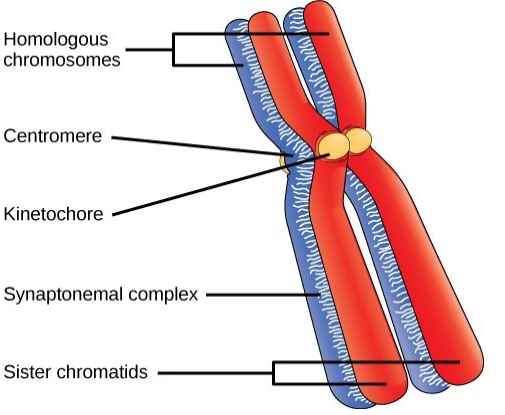
Explain The Structure Of Chromosomes With Diagrams Class 12 Biology Cbse

The Organization And Control Of Eukaryotic Genomes Ppt Download
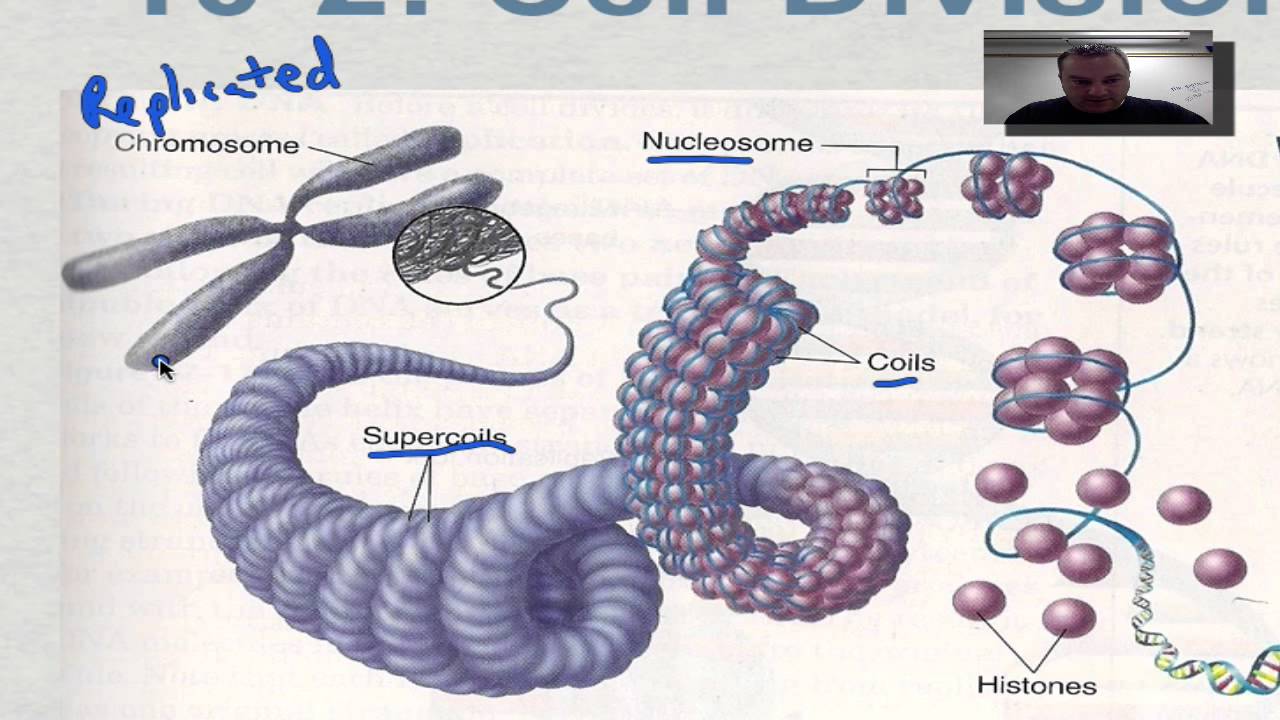
Chapter 10 Part 3 Eukaryotic Chromosomes Youtube

Chromosomes Definition Structure Types Model Functions

Eukaryotic Chromosome Organization Lecture Ii Ppt Video Online Download

1 The Eukaryotic Chromosomal Organization The Steps Showing The Download Scientific Diagram

Eukaryotic Chromosome Organization Chromosome Organization If All Of The Dna Was Stretched Out It Would Measure 1 8 Metres In Length How Does It Ppt Download

Explain The Structure Of An Eukaryotic Chromosome Brainly In

Dna Packaging In Eukaryotes And Prokaryotes Biology For Majors I

Comments
Post a Comment